Table of Contents
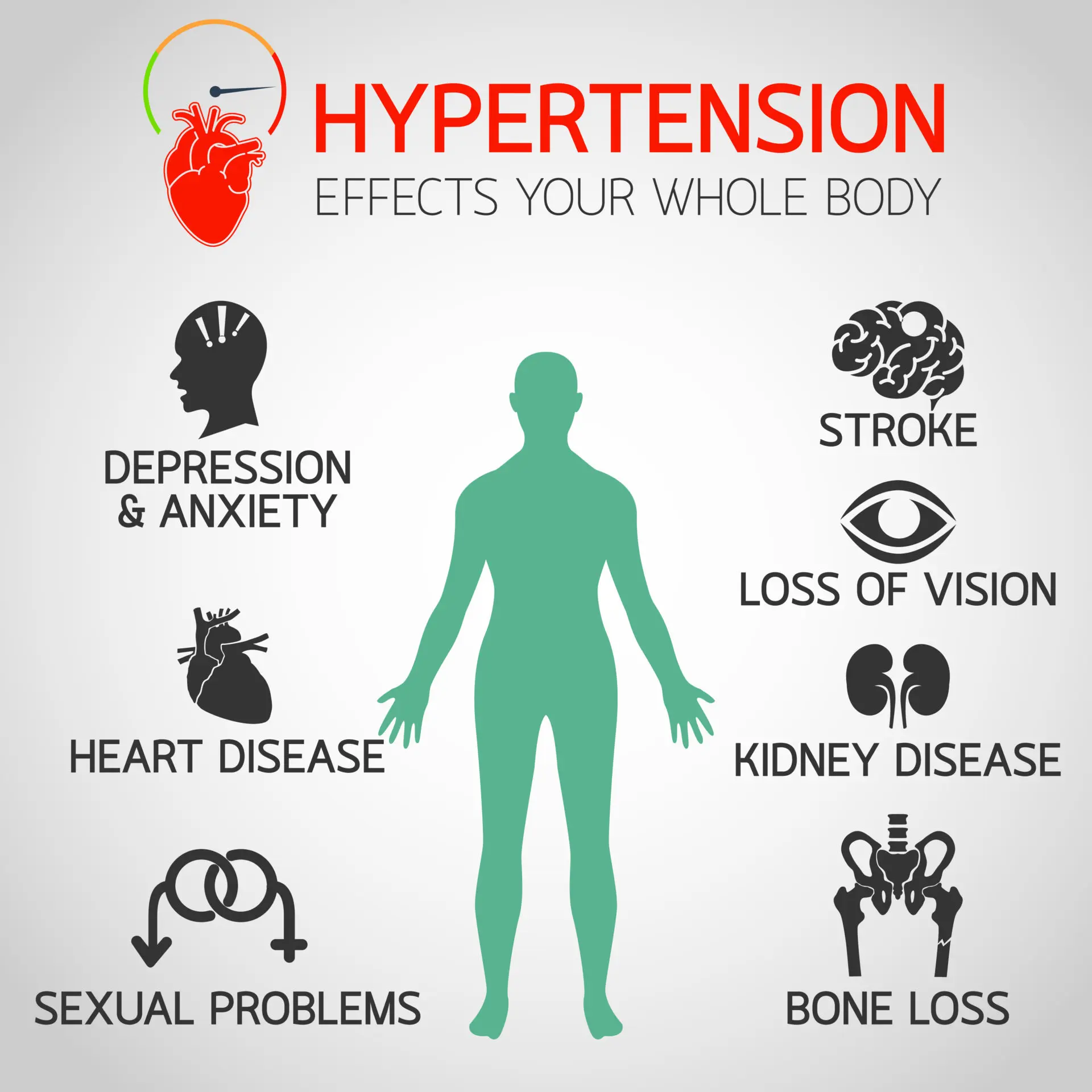
What is Hypertension (HTN)?
High blood pressure (HTN), also known as hypertension or silent killer, can silently affect the body for years before symptoms appear. Without treatment, high blood pressure can lead to disability, a lower quality of life, or even a heart attack and stroke.
Generally, hypertension is defined as a blood pressure of 130 over 80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) or higher.
When blood pressure is high, it can damage the walls of the arteries and blood vessels over time which can lead to dangerous complications and even death if left untreated.
How does HTN cause vascular damage?
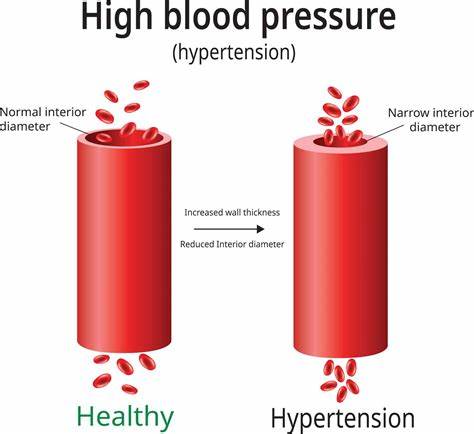
Healthy arteries are flexible, strong, and elastic with smooth inner lining, allowing blood to flow freely, supplying vital organs and tissues with nutrients and oxygen.
Over time, hypertension increases the force of blood flow through the arteries it starts to damage the walls of the arteries.
Arterial Damage and Narrowing:
Vascular damage begins with small tears in the arterial walls. As these tears start to form, LDL cholesterol flowing through the blood begins to attach to the torn area. Increasing amounts of cholesterol deposit on the arterial walls, narrowing the inner surface of the artery. This occurrence restricts blood flow throughout the body.
Aneurysm:
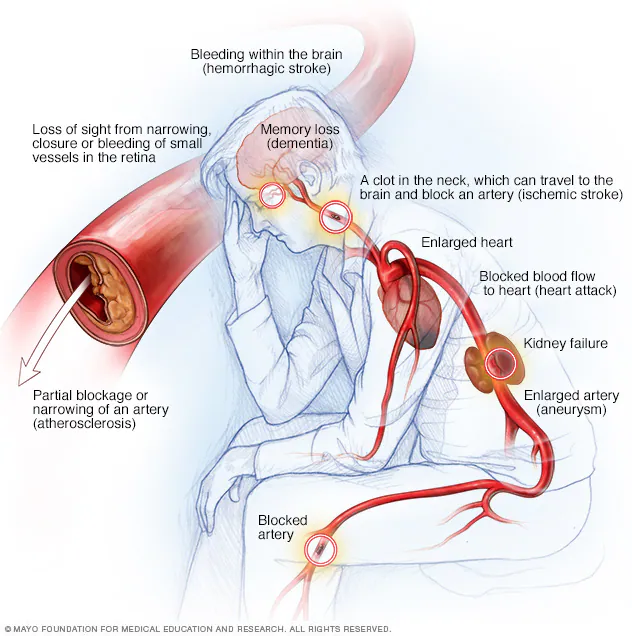
Over time, the constant pressure of blood moving through a weakened artery can cause a bulging and dilation (widening) of arterial wall called an aneurysm. It can form in any artery but is more common in the largest artery in the body, called the aorta. An aneurysm can rupture, causing life-threatening internal bleeding.
Effects of Hypertension on the Coronary Blood Vessels (Supplying Heart)
Coronary Artery Disease:
Hypertension can narrow the arteries and damage those that supply blood to the heart which is known as coronary artery disease (CAD). Very low blood flow to the heart can lead to chest pain called angina that can cause irregular heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias, leading to a heart attack.
Effects of HTN on Brain Blood Vessels
High blood pressure may play a role in the development of dementia over time. Reduced blood flow to the brain due to high blood pressure causes memory, thinking, or concentration problems.
Stroke:
A stroke occurs when part of the brain does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, or when there is bleeding inside or around the brain. These issues cause brain cells to die. Damaged blood vessels due to HTN can become narrowed, ruptured, or leaked. Hypertension can also cause blood clots to form in the arteries leading to the brain which can block blood flow to the brain and increase the risk of stroke.
Effects of Hypertension on Bones
High blood pressure can lead to the loss of bone density, called osteoporosis. Women who have gone through menopause are particularly at risk for developing high blood pressure and osteoporosis.
Effects of Hypertension on the Kidneys:
It can damage small blood vessels and lead to kidney damage. Damaged blood vessels prevent the kidneys from effectively filtering waste materials from the blood. These events allow dangerous levels of fluids and waste materials to accumulate in the body. When the kidneys do not function properly enough, this constitutes a serious condition known as kidney failure.
Effects of Hypertension on the Eyes:
Hypertension can damage small and delicate blood vessels that supply blood to the eye (retina), leading to the following conditions:
- Damage to the blood vessels in the retina (retinopathy)
- Accumulation of fluid under the retina (choroidopathy)
- Damage to the optic nerve, also known as optic neuropathy. This damage can lead to bleeding inside the eye or loss of vision.
Note: Having diabetes (high blood sugar disease) along with high blood pressure increases the risk of developing retinopathy.
Effects of HTN on Sexual Activity and Reproduction:
Sexual organs rely on the extra blood flow generated during sexual arousal. When high blood pressure causes blockages in the blood vessels leading to the genital organs or vagina, sexual dysfunction may occur.
Men may experience prolonged times to achieve and maintain erection, while women may experience issues such as decreased sexual arousal, vaginal dryness, and difficulty achieving orgasm.